What is COPD?
COPD is a progressive lung disease where the breathing tubes (bronchioles) and air sacs (alveoli) of your lungs have been damaged. It is also commonly referred to as emphysema or chronic bronchitis. It is a serious illness that can cause distressing symptoms and intermittent infections (exacerbations) that may be life-threatening.
What causes COPD?
The most common cause for COPD is smoking. COPD may develop years after you have stopped smoking. You may also develop COPD from passive smoking, where you breathe in the smoke from others over time. Although, this is uncommon. Occasionally, COPD can be caused by breathing in toxic fumes. In rare cases, COPD is caused by a genetic problem.
What are the symptoms of COPD?
Damage to the bronchioles causes narrowing and difficulty moving air in and out of your lungs. amage to the alveoli reduces the ability of your lungs to transfer oxygen from the air into your bloodstream. As a result, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Cough and phlegm
- Chest tightness
In the early stages of COPD you may have mild or no symptoms at all. With early assessment and treatment, your disease progression can be altered. However, with COPD you are at an increased risk for:
- Chest infections, which can lead to exacerbations of COPD
- Lung cancer
- Heart problems
What tests are there for COPD?
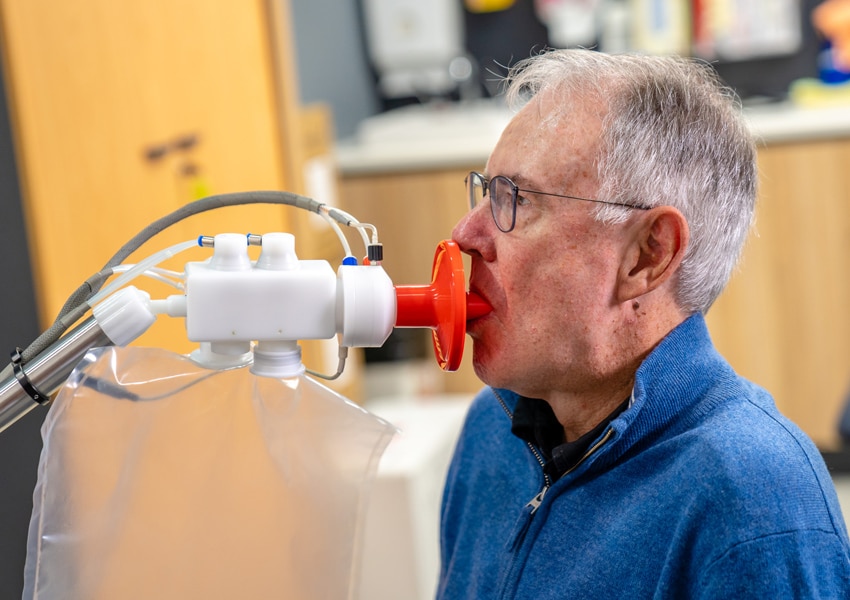
The diagnosis of COPD is based on a Lung function test. This will also determine the severity of your condition.
Depending on your symptoms, other tests that may be performed include:
Blood tests
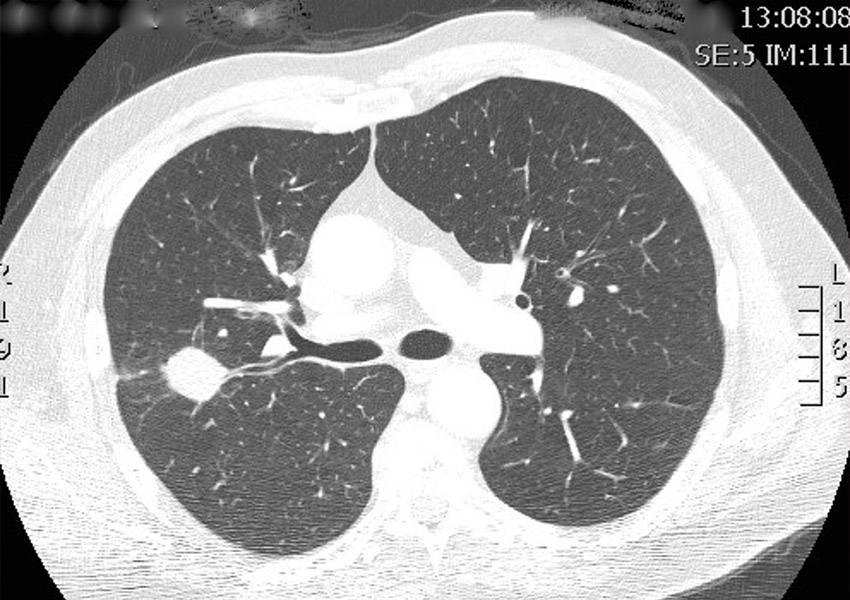
- Chest X-ray and/or CT scan of the chest
- Walking test to check your oxygen levels during activity
- Electrocardiogram and/or echocardiogram to evaluate your heart function
- Phlegm (sputum) sample to test for infection
How we can help you
The diagnosis and treatment of COPD is rapidly evolving. COPD cannot be cured or reversed, however there are a number of treatments that can improve your symptoms, enhance your breathing and maximise your quality of life. These will reduce your risk of having an exacerbation. These treatments include:
- Quit smoking. If you smoke or vape, this is the most important thing you can do.
- Get the flu shot every year and have your pneumonia vaccine.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation. This is a very useful program that will teach you helpful exercises, breathing techniques, and ways to manage your symptoms. Our expert respiratory physiotherapists at Lung and Sleep can help you with this.
- Inhalers. There are a lot of inhaler medications available for COPD. Our specialists will help you select the best treatment for your individual needs.
- Steroids and antibiotics may be required if you have an exacerbation of COPD.
- Oxygen may be helpful if your COPD is severe enough to cause low oxygen levels
- If your COPD is severe, advanced treatments including surgery may be beneficial in very special situations but are not without risk.
The right treatment combination will give you the most benefit while avoiding unwanted side effects. Our physicians at Lung and Sleep have a depth of expertise in this area and will devise a personalised treatment plan to optimise your lung health.